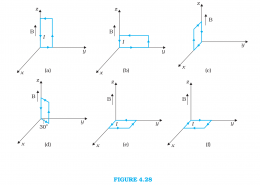
When can liquid be in equilibrium ? 1 What is the effect of gravity on pressure ? 1 What is the cause of excess pressure inside a soap bubble ? 1 Three containers have different area on the top surface and same base ...
Tiwari Academy Discussion Latest Questions
Class 11 physics Chapter 13 Kinetic Theory NCERT Class 11 physics Chapter 13 Class 11 physics Chapter 13 physics Class 11 Notes Chapter 13 CBSE Class 11 physics Science solutions 2022-2023 Class 11 physics Science study 2022-2023 Class ...
Class 11 physics Chapter 1 Units and Measurements NCERT Class 11 physics Chapter 1 Class 11 physics Chapter 1 physics Class 11 Notes Chapter 1 CBSE Class 11 physics Science solutions 2022-2023 Class 11 physics Science study 2022-2023
Class 11 physics Chapter 11 System of particles and rotational motion notes NCERT Class 11 physics Chapter 11 Class 11 physics Chapter 11 physics Class 11 Notes Chapter 11 CBSE Class 11 physics Science solutions 2022-2023 Class 11 ...
Class 11 physics Chapter 7 System of particles and rotational motion notes NCERT Class 11 physics Chapter 7 Class 11 physics Chapter 7 physics Class 11 Notes Chapter 7 CBSE Class 11 physics Science solutions 2022-2023 Class 11 ...
Class 11 physics Chapter 12 Thermodynamics NCERT Class 11 physics Chapter 12 Class 11 physics Chapter 12 physics Class 11 Notes Chapter 12 CBSE Class 11 physics Science solutions 2022-2023 Class 11 physics Science study 2022-2023 Class ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Science Work energy and power 4 Important Board Questions Work energy and power NCERT Books for Session 2022-2023 CBSE Board and UP Board 2 Marks Questions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Science Work energy and power 4 Important Board Questions Work energy and power NCERT Books for Session 2022-2023 CBSE Board and UP Board 2 Marks Questions
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Science Work energy and power 4 Important Board Questions Work energy and power NCERT Books for Session 2022-2023 CBSE Board and UP Board 2 Marks Questions